Memory Unit
Computer Memory Units definition
Primary storage, or memory, implies the space on your hard drive that is quickly utilized for working space. This generally happens in a chip. The memory comprises four kinds of memory chips RAM, ROM, CMOS, and glimmer. RAM represents random access memory and ROM represents read-only memory. these are likewise called the primary memory of a computer.Computer Memory Unit list
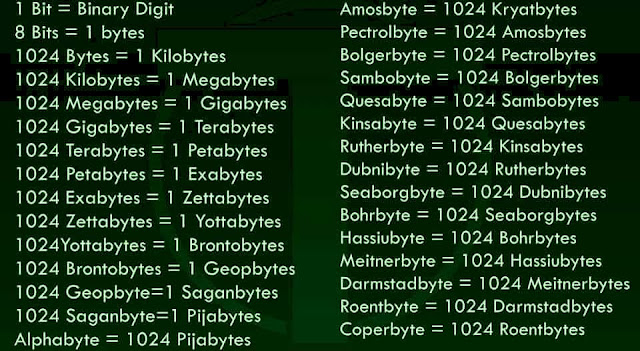
1 bit (binary digit*) = the value of 0 or 18 bits = 1 byte1024 bytes = 1-kilo byte 1024 kilobytes = 1 megabyte1024 megabytes =1 gigabyte1024 gigabytes =1 terabyte1024 terabytes =1 petabyte
- Truncations
1 kilobyte = 1 KB
1 megabyte = 1 MB
1 gigabyte = 1 GB
1 terabyte = 1 TB
1 petabyte = 1 PB
- Size in "bytes"
Kilobyte (KB) = 1,024
Megabyte (MB) = 1,048,576
Gigabyte (GB) = 1,073,741,824
Terabyte (TB) = 1,099,511,627,776
Petabyte (PB) = 1,125,899,906,842,624
- Clarifications and NOTES
The Decimal System is a base 10 number framework that utilizations ten digits (0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9).
1000 is accomplished as pursues:
1 x10 = 10 x 10 = 100 x 10 = 1000 (kilo)
The Binary System is a base 2 number framework that utilizations just two (bi) numbers or digits (0 and 1) to speak to all qualities.
The unit nearest to 1000 is accomplished as pursues:
1 byte x 2 = 2
x 2 = 4
x 2 = 8
x 2 = 16
x 2 = 32
x 2 = 64
x 2 = 128
x 2 = 256
x 2 = 512
x 2 = 1,024 bytes (1 kilobyte)
A "2 gig hard drive" signifies the drive holds "2 gigabytes" (2,147,483,648 bytes). Only one CD can hold 650 MB, so 2 GB could be loaded up with around 3 CDs.
Terabyte databases are getting normal, and talk has it that there are most likely a couple of petabyte databases in the United States Pentagon.
Computer Memory Units Table
Computer Memory Unit nibble
1.0 or 1
2.Bit
3.Nibble
4.Byte
5.Octet
6.Kilobyte
7.Megabyte
8.Gigabyte
9.Terabyte
10.Petabyte
11.Exabyte
12.Zettabyte
13.Yottabyte
2.Bit
3.Nibble
4.Byte
5.Octet
6.Kilobyte
7.Megabyte
8.Gigabyte
9.Terabyte
10.Petabyte
11.Exabyte
12.Zettabyte
13.Yottabyte
What is Computer Memory Unit
Bit
The littlest unit of information in a computer is called Bit (Binary Digit). A piece has a solitary parallel worth, either 0 or 1. In The Maximum Computer systems, there are eight bits in a byte. The estimation of a piece is normally put away as either above or underneath an assigned degree of electrical charge in a solitary capacitor inside a memory gadget.
Nibble
A large portion of a byte (four bits) is known as a Nibble.
Byte
The computer systems, a byte is a unit of data that is eight parallel digits long. A byte is a unit most computers use to address a character, for instance, a letter, number or typographic picture (for example, "g", "5", or "?"). A byte can similarly hold a progression of bits that ought to be used in some greater unit of usage purposes (for example, the surge of bits that involve a visual picture for a program that exhibits pictures or the arrangement of bits that sets up the machine code of a computer program).
In some computer systems, four bytes establish a word, a unit that a computer processor can be intended to deal with proficiently as it peruses and forms every guidance. Some computer processors can deal with two-byte or single-byte guidelines.
A byte is truncated with a "B". (A piece is contracted with a little "b"). Computer storage is typically estimated in byte products. For instance, an 820 MB hard drive holds an ostensible 820 million bytes – or megabytes – of information. Byte products depend on powers of 2 and regularly communicated as an "adjusted" decimal number. For instance, one megabyte ("one million bytes") is really 1,048,576 (decimal) bytes.
Octet
In certain systems, the term octet is utilized for an eight-piece unit rather than a byte. In numerous systems, four eight-piece bytes or octets structure a 32-piece word. In such systems, directions lengths are now and again communicated as full-word (32 bits long) or half-word (16 bits long).
Kilobyte
A Kilobyte is roughly a thousand bytes (really, 2 to the tenth power, or decimal 1,024 bytes).
Megabyte
As an extent of PC processor stockpiling and veritable and virtual memory, a megabyte (contracted MB) is 2 to the twentieth power byte or 1,048,576 bytes in decimal documentation.
Gigabyte
A Gigabyte (articulated Gig-a-chomp with hard G's) is a proportion of computer information storage limit and is "around" a billion bytes. A gigabyte is two to the 30th power or 1,073,741,824 in decimal documentation.
Terabyte
A Terabyte is a proportion of the computer storage limit and is 2 to the 40th power of 1024 gigabytes.
Petabyte
A Petabyte (PB) is a proportion of memory or storage limit and is 2 to the 50th power bytes or, in decimal, roughly a thousand terabytes (1024 terabytes).
Exabyte
An Exabyte (EB) is a huge unit of computer information storage, two to the sixtieth power bytes. The prefix exa implies one billion, or one quintillion, which is a decimal term. Two to the sixtieth power is really 1,152,921,504,606,846,976 bytes in decimal, or to some degree over a quintillion (or ten to the eighteenth power) bytes. It isn't unexpected to state that an Exabyte is roughly one quintillion bytes. In decimal terms, an Exabyte is a billion gigabytes.
Zettabyte
A Zettabyte (ZB) is equivalent to one sextillion bytes. It is generally truncated ZB. Right now, no computer has one Zettabyte of storage. It has 1024 Exabytes.
Yottabyte
A Yottabyte is equivalent to one septillion bytes. It is generally truncated YB. Right now, no computer has one Zettabyte of storage. It has 1024 Zettabytes.
Computer Memory Units in ascending order
RAM
RAM represents Random Access Memory and is a kind of chip utilized in primary storage memory. It is likewise impermanent storage, holding programming guidelines and transient working memory for the processor. RAM can be expanded in many computers by utilizing the expandable memory spaces.
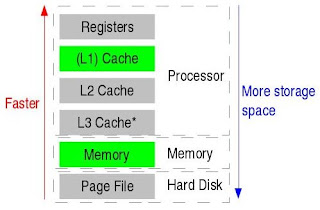
Primary storage
Primary storage (RAM)is called 'primary' since it is the fundamental memory that is accessible to the CPU. It is utilized to store data that is as of now being utilized.
Random-access memory
Random-access memory or RAM is a type of data storage utilized in computers. Taken as incorporated circuits that speak to primary or impermanent storage, it permits data which is put away to be accessed in any request, which is the reason it's called random. Making it random rather than successive extraordinarily speeds up the computer can work since time isn't squandered setting off to where required data is put away (as in tape reinforcements). Random_access_memory
In arbitrary access memory(RAM) the memory cells can be gotten to for data move from any desired irregular area. That is, the way toward finding a word in memory is the equivalent and requires an equivalent measure of time regardless of where the phones are found physically in memory.
Correspondence among memory and its condition are accomplished through data input and yield lines, address determination lines, and control lines that indicate the bearing of the move.
A square outline of a RAM unit is demonstrated as follows:
Random Access Memory
The n data input lines give the data to be stored in memory, and the n data yield lines supply the data leaving specific word picked among the 2k accessible inside the memory. The two control inputs determine the course of move desired.
Smash: Write and Read Operations
The two activities that an arbitrary access memory can perform are the write and read tasks. The write signal indicates exchange inactivity and the read sign determines an exchange out the activity. On tolerating one of these control signals. The inward circuits inside the memory give the desired capacity. The means that must be taken to move another word to be stored into memory are as per the following:
Apply the twofold address of the desired word into the address lines.
Apply the data bits that must be stored in memory into the data input lines.
Initiate the write input.
The memory unit will at that point take the bits by and by accessible in the input data lines and store them in the predefined by the address lines. The means that must be taken to move a stored word out of memory are as per the following:
Apply the double address of the desired word into the address lines.
Enact the read input.
The memory unit will at that point take the bits from the word that has been chosen by the address and apply them into the yield data lines. The substance of the chose word doesn't change in the wake of reading.
Volatile
Unstable is a graphic word for RAM which is momentary memory; when the computer loses control the impermanent storage will be lost. So as to keep data from being lost, it must be spared to a hard plate or lasting storage zone called ROM (Read Only Memory)
Fast
RAM (by and large) works quicker than a hard drive, and a few, quicker than streak memory (which isn't unpredictable). This more noteworthy speed is the reason it's as yet utilized in computers today. Computers will run quicker and all the more proficiently with more RAM. The recommended measure of RAM for current working frameworks, for example, Windows Vista/XP and OSX 10.5 to run easily with the heaviness of shared illustrations memory and programs is 1024 megabytes (1GB). As of now, RAM comes in 4 sorts: DDR1, DDR2, DDR3 and DDR4 accessible since 2014. DDR1 and 2 areas of now generally utilized. DDR3 works at a higher recurrence and has 3 data move channels consequently expanding transfer speed. Recently created SSD hard plates right now are equipped for meeting and surpassing the exchange pace of DDR and DDR2.
A 32bit working framework is only equipped for using 4gb of RAM. Be that as it may, a 64bit working framework is fit for supporting significantly more memory. When contrasted with ROM, RAM is costlier.
ROM
ROM (Read Only Memory) alludes to a read-only memory chip that can't be composed on or eradicated by the computer client without uncommon hardware. While utilizing ROM substance is not lost when the capacity to the computer is never again accessible.
Since it needn't bother with control, and can't be modified the only things put on ROM are beginning (booting) guidelines.
CMOS
CMOS represents a Complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor. This is an innovation utilized in chips and simple circuits. Cmos
It doesn't lose it's a substance when killed regardless of whether the substance was not spared. It additionally keeps the time and dates current in any event, when the computer is killed.




























No comments:
Post a Comment
IF YOU HAVE ANY DOUBTS, PLEASE LET ME KNOW